What Are Dexterous Hands? Technical Insights into Robotic Mastery
2026-01-16
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 {
font-family: Verdana, Helvetica, "Times New Roman", Arial, sans-serif;
color: #333;
line-height: 1.6;
padding: 15px;
max-width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0__title {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 1em;
color: #0056b3;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0__subtitle {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-top: 1.5em;
margin-bottom: 0.8em;
color: #007bff;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 p {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 1em;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 strong {
font-weight: bold;
color: #007bff;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 [data-testid="image-viewer"] {
margin-top: 1.5em;
margin-bottom: 1.5em;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 [data-testid="image-viewer"] > div:last-child > div {
font-size: 12px;
color: #666;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 0.5em;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 ul {
list-style: none !important;
padding-left: 0;
margin-bottom: 1em;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 ul li {
list-style: none !important;
position: relative;
padding-left: 20px;
margin-bottom: 0.5em;
font-size: 14px;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 ul li::before {
content: "•" !important;
position: absolute !important;
left: 0 !important;
color: #007bff;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 ol {
list-style: none !important;
padding-left: 0;
margin-bottom: 1em;
counter-reset: list-item;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 ol li {
list-style: none !important;
position: relative;
padding-left: 25px;
margin-bottom: 0.5em;
font-size: 14px;
counter-increment: none;
}
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 ol li::before {
content: counter(list-item) "." !important;
position: absolute !important;
left: 0 !important;
width: 20px;
text-align: right;
color: #333;
font-weight: bold;
line-height: 1;
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.gtr-container-d3x7r0 {
padding: 30px;
max-width: 960px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
}
What Are Dexterous Hands? Technical Insights into Robotic Mastery
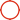
Ever wondered how a robot could delicately peel an orange or assemble a smartphone? That's the realm of dexterous hands—highly agile, multi-jointed appendages designed for intricate manipulation. In technical terms, a dexterous hand is an end-effector with multiple degrees of freedom (DOF), sensors, and actuators enabling dexterous manipulation, dexterous grasping, and fine motor control. While inspired by the human hand's 21 DOF, robotic versions push boundaries in precision and endurance. This article explores what dexterous hands are, their evolution from past to future, key applications, China's pioneering breakthroughs, major brands, and how our company supplies a wide range of dexterous robotic hands for diverse needs.
Shadow Dexterous Hand Series - Research and Development Tool
The Past: Origins of Dexterous Hands
The journey of dexterous hands began in the mid-20th century with early mechanical grippers for industrial automation. In the 1960s, Stanford's "Stanford Hand" introduced basic multi-fingered designs, but they were rigid and limited to simple grasps. By the 1980s, Japan's dexterous robotic hands like the Utah/MIT Hand added tactile sensors and 16 DOF, enabling early anthropomorphic dexterous hand prototypes for research. These paved the way for multi-fingered dexterous hands, focusing on mimicking human kinematics but struggling with control complexity and power efficiency. Historically, they were confined to labs, handling tasks like object reorientation in controlled environments.
The Present: Current Technology and Applications
Today, dexterous hands combine advanced actuators (servo or pneumatic), high-resolution sensors (force, torque, tactile), and AI-driven algorithms for real-time adaptation. A typical robotic dexterous hand has 15-24 DOF, allowing dexterous grasping of irregular objects with slip detection and force feedback.
How they work: Actuators drive finger joints, while embedded sensors (e.g., capacitive arrays) provide haptic data. AI models like reinforcement learning optimize dexterous manipulation for tasks requiring sub-millimeter precision.
Current scenarios:
Manufacturing: In automotive assembly, dexterous robotic hands handle delicate wiring or part insertion, reducing errors in high-mix production.
Healthcare: Prosthetic dexterous hand prosthetics restore fine motor skills for amputees, with myoelectric interfaces reading muscle signals.
Space Exploration: NASA's rovers use multi-fingered dexterous hands for sample collection on Mars, enduring radiation and dust.
Daily Assistance: Home robots with anthropomorphic dexterous hands assist elderly users in grasping utensils or medication.
These applications highlight versatility, but challenges like battery life and cost persist.
TESOLLO unveils dexterous robot hand for humanoids
The Future: Emerging Trends and Scenarios
Looking ahead, dexterous hands will integrate soft robotics (e.g., silicone-based for safer human interaction) and brain-computer interfaces for intuitive control. Expect 30+ DOF models with self-healing materials and swarm intelligence for collaborative tasks.
Future uses:
Autonomous Surgery: Dexterous robotic hands performing minimally invasive procedures with haptic feedback.
Disaster Response: Navigating rubble to rescue victims or defuse hazards.
Consumer Robotics: Affordable dexterous hands in household bots for cooking or childcare.
Metaverse Integration: Virtual dexterous manipulation syncing with physical hands for remote work.
Advancements in nanomaterials and edge AI will make them lighter, smarter, and more affordable.
China's Breakthroughs and Advantages in Dexterous Hands
China leads in dexterous robotic hand innovation, leveraging massive R&D investment and a vast manufacturing ecosystem. Key breakthroughs include:
F-TAC Hand (Peking University/BIGAI): The world's first with full-hand high-resolution tactile sensing (10,000 pixels/cm², 70% palm coverage) and complete dexterity. How it works: Integrates flexible sensors without sacrificing motion; ideal for uncertain environments like parcel sorting. Select for apps needing adaptive grips—pair with AI for real-time adjustments in logistics or assembly.
PaXini Tech's Tactile Hand: Developed by a young Shenzhen team, features 1,140 sensing units detecting 15 dimensions (force, texture, humidity). Selection guide: Opt for this in high-precision tasks; calibrate sensors for slip detection in e-commerce fulfillment centers.
Wuji Hand (WUJI Tech/Pan Motor): A 600g marvel with 20 joints, lifting 20kg while cutting scissors delicately. Priced at $5.5K, it's direct-drive for robustness. How to choose: For strength-focused apps like warehouse handling; integrate with humanoid robots for heavy-duty dexterous grasping.
China's advantages: Cost-effective scaling (half global market share), superior tactile tech, and market-driven innovation. With 60+ companies, domestic supply chains cut costs 30-50% vs. Western rivals, accelerating commercialization in humanoid robots and automation.
Major Brands of Dexterous Robotic Hands
Leading brands offer varied options—here's how to select:
Shadow Robot (UK): Flagship Shadow Dexterous Hand with 24 movements/20 DOF. Selection: For research; calibrate for teleoperation in nuclear handling.
TESOLLO (South Korea): Affordable, high-dexterity models. Choose for: Humanoid integration; test DOF for assembly tasks.
Agile Robots (Germany/China): Agile Hand with 21 joints/15-16 DOF. Guide: Modular fingers suit delicate ops; program for AI-driven grasping in manufacturing.
Inspire Robots (China): Micro-actuated hands with hybrid force control. Selection: For precision; integrate sensors for surgical robots.
Dexterity (USA): AI-powered superhumanoids. How to pick: For logistics; leverage vision-touch fusion in warehouses.
Other notables: Allegro Hand (Wonik Robotics), Dextrous Hand (Robotiq), and startups like Contactile or Apicoo for specialized tactile or safety features.
Our Company: Your Source for Diverse Dexterous Hand Solutions
At our company, we specialize in providing a rich portfolio of dexterous hands from top brands like Shadow, Inspire, and Wuji. Whether you need a multi-fingered dexterous hand for R&D or an anthropomorphic dexterous hand for production, we offer customized selection, integration support, and training. Contact us for expert guidance on dexterous robotic hand setups tailored to your industry.
Keywords: dexterous hands, robotic dexterous hands, dexterous manipulation, anthropomorphic dexterous hand, multi-fingered dexterous hand, dexterous grasping, dexterous hand prosthetics, dexterous hand applications, Chinese dexterous robotic hands, F-TAC Hand, Wuji Hand.
View More
What Is a Dexterous Hand? Fun Guide to Robotic Mastery and Human Magic
2025-12-31
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 {
font-family: Verdana, Helvetica, "Times New Roman", Arial, sans-serif;
color: #333;
line-height: 1.6;
padding: 15px;
box-sizing: border-box;
max-width: 100%;
overflow-x: hidden;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 p {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 1em;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 strong {
font-weight: bold;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-heading-main {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 1.5em;
color: #0056b3;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-heading-2 {
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-top: 2em;
margin-bottom: 1em;
color: #0056b3;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-heading-3 {
font-size: 15px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-top: 1.5em;
margin-bottom: 0.8em;
color: #0056b3;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ul,
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ol {
margin: 1em 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ul li,
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ol li {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 0.5em;
position: relative;
padding-left: 20px;
text-align: left;
list-style: none !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ul li::before {
content: "•" !important;
position: absolute !important;
left: 0 !important;
color: #007bff;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ol li::before {
content: counter(list-item) "." !important;
position: absolute !important;
left: 0 !important;
color: #007bff;
font-weight: bold;
line-height: 1;
width: 18px;
text-align: right;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ol {
counter-reset: list-item;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 ol li {
counter-increment: none;
list-style: none !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 img {
height: auto;
display: block;
margin: 1em auto;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-image-caption {
font-size: 12px;
color: #666;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 0.5em;
margin-bottom: 1.5em;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-table-wrapper {
width: 100%;
overflow-x: auto;
margin: 1.5em 0;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 table {
width: 100%;
border-collapse: collapse !important;
border-spacing: 0 !important;
margin: 0 !important;
font-size: 14px;
min-width: 600px;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 th,
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 td {
border: 1px solid #ccc !important;
padding: 8px 12px !important;
text-align: left !important;
vertical-align: top !important;
word-break: normal;
overflow-wrap: normal;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 th {
background-color: #f0f0f0;
font-weight: bold !important;
color: #333;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 tbody tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 {
padding: 25px 50px;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-heading-main {
font-size: 24px;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-heading-2 {
font-size: 20px;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-heading-3 {
font-size: 18px;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 table {
min-width: auto;
}
.gtr-container-f7h2k9 .gtr-table-wrapper {
overflow-x: visible;
}
}
What Is a Dexterous Hand? Fun Guide to Robotic Mastery and Human Magic
Imagine a hand that can juggle eggs without cracking them, play a guitar solo, or assemble tiny circuit boards in the dark. That's the magic of a dexterous hand—a term buzzing in robotics and engineering circles. But what exactly is it? In simple terms, a dexterous hand refers to a highly agile, multi-fingered appendage capable of intricate movements, whether it's your own human hand or a cutting-edge robotic dexterous hand. This article dives into the world of dexterous hands, blending tech facts with fun analogies to make it easy to grasp. We'll explore why these marvels exist, how they work, and their game-changing applications—all while packing in keywords like anthropomorphic dexterous hand, multi-fingered dexterous hand, and dexterous manipulation for that SEO boost.
Shadow Robot | Dexterous Robotic Hands & Teleoperated Robots
The Human Dexterous Hand: Nature's Original Masterpiece
Your hand is the ultimate dexterous hand prototype—think of it as a Swiss Army knife with fingers. With 27 bones, 34 muscles, and over 100 ligaments, it boasts 21 degrees of freedom (DOF), allowing twists, grips, and pinches. Why do we need such a dexterous human hand? Evolution wired it for survival: picking berries, crafting tools, or high-fiving friends.
Key features:
Tactile Sensing: Thousands of nerves detect texture, temperature, and pressure—like a built-in radar for "is this hot coffee or a fluffy kitten?"
Opposable Thumb: The star player for dexterous grasping, letting you tie shoelaces or scroll TikTok.
Fine Motor Skills: Enables dexterous manipulation for tasks like threading a needle.
Fun fact: Without our dexterous hands, we'd still be fumbling like T-Rexes. But humans aren't the only ones—enter the robots!
Robotic Dexterous Hand: Sci-Fi Comes to Life
A robotic dexterous hand is an engineered wonder mimicking the human version, designed for robots to handle complex tasks. Unlike simple grippers (think claw machines), a dexterous robotic hand has multiple fingers, joints, and sensors for human-like agility. Pioneered in labs like MIT's, these hands can reorient over 2,000 objects or operate in pitch-black using touch alone.
Why build them? Robots need dexterous hands to conquer real-world chaos—picking fragile items, assembling gadgets, or exploring space. Top models like the Shadow Dexterous Hand (with 20 DOF) or Columbia's touch-savvy version show how far we've come.
TESOLLO unveils dexterous robot hand for humanoids
Tech Breakdown: What Makes a Dexterous Robotic Hand Tick?
Picture a multi-fingered dexterous hand as a high-tech puppet. Core components:
Degrees of Freedom (DOF): 15-24 per hand for fluid motion—more DOF means smoother dexterous grasping.
Sensors Galore: Force, torque, and tactile sensors act like "skin," detecting slip or pressure for adaptive grips.
Actuators and Motors: Tiny servos or pneumatics power each joint, controlled by AI algorithms.
AI Brains: Machine learning enables dexterous manipulation, learning from trials like a kid stacking blocks.
Compared to basic robot claws, anthropomorphic dexterous hands (human-shaped) excel in versatility but cost more—up to $50,000 per unit!
Feature
Human Dexterous Hand
Robotic Dexterous Hand
DOF
21
15-24
Sensing
Nerves & Skin
Tactile Sensors
Power Source
Muscles
Electric/Pneumatic
Learning
Brain Experience
AI Algorithms
Cost
Free (with body!)
$10K-$100K+
Why Dexterous Hands Matter: Real-World Wins
Dexterous hands aren't just lab toys—they're revolutionizing industries:
Robotics: Tesla's Optimus uses dexterous robotic hands for folding laundry or sorting parts—bye-bye, assembly line boredom!
Medical Prosthetics: Advanced dexterous hand prosthetics restore independence, with myoelectric controls reading muscle signals.
Space & Exploration: NASA's rovers with multi-fingered dexterous hands grab Martian rocks without fumbling.
Everyday Helpers: Imagine a home robot with dexterous grasping skills chopping veggies or playing piano duets.
Challenges? High costs, complex control (AI still lags human intuition), and durability in harsh spots like factories.
Highly Dexterous Robot Hand Can Operate in the Dark — Just Like Us ...
The Future of Dexterous Hands: Smarter, Softer, Superhuman?
By 2030, expect dexterous hands with soft materials (like squishy gels) for safer human-robot hugs, or brain-computer interfaces for mind-controlled dexterous manipulation. Companies like Shadow Robot and TESOLLO are pushing boundaries, making anthropomorphic dexterous hands affordable and ubiquitous.
In short, a dexterous hand is the bridge between clunky machines and graceful helpers. Whether human or robotic, it's all about turning "impossible" tasks into everyday feats. Curious about building one? Dive into robotics kits—your own dexterous robotic hand adventure awaits!
Related searches: dexterous hand robotics, dexterous hand prosthetics, dexterous hand DOF, dexterous hand sensors, dexterous hand applications, dexterous hand AI control.
View More
What Are Welding Cobots? The Complete 2025 Guide to Collaborative Welding Robots
2025-12-03
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 {
font-family: Verdana, Helvetica, "Times New Roman", Arial, sans-serif;
color: #333;
line-height: 1.6;
padding: 15px;
box-sizing: border-box;
max-width: 100%;
overflow-x: hidden;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 .gtr-title-main {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 20px;
text-align: left;
color: #0056b3;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 .gtr-title-section {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-top: 30px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
text-align: left;
color: #0056b3;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 p {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
text-align: left !important;
line-height: 1.6;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 .gtr-image-wrapper {
margin-top: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 img {
/* As per strict instruction: "禁止新增任何布局或尺寸样式",
max-width: 100%; height: auto; are omitted.
Images will display at their intrinsic size or size specified by HTML attributes,
potentially overflowing on smaller mobile screens. */
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 ul,
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 ol {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none !important;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 li {
list-style: none !important;
position: relative;
padding-left: 25px;
margin-bottom: 8px;
font-size: 14px;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 ul li::before {
content: "•" !important;
color: #007bff;
font-size: 1.2em;
position: absolute !important;
left: 0 !important;
top: 0;
line-height: 1.6;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 ol {
counter-reset: list-item;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 ol li::before {
/* As per strict instruction: "禁止写 counter-increment: none;",
this will result in the ordered list displaying "1. 1. 1. ..." */
content: counter(list-item) "." !important;
position: absolute !important;
left: 0 !important;
top: 0;
width: 18px;
text-align: right;
margin-right: 5px;
color: #007bff;
font-weight: bold;
line-height: 1.6;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 .gtr-table-wrapper {
overflow-x: auto;
margin-top: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 table {
width: 100%;
border-collapse: collapse !important;
border-spacing: 0 !important;
margin: 0;
font-size: 14px;
min-width: 600px;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 th,
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 td {
border: 1px solid #ccc !important;
padding: 10px !important;
text-align: left !important;
vertical-align: top !important;
word-break: normal;
overflow-wrap: normal;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 th {
font-weight: bold;
background-color: #e9ecef;
color: #333;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 tbody tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f9f9f9 !important;
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 {
max-width: 960px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 .gtr-title-main {
font-size: 24px;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 .gtr-title-section {
font-size: 20px;
}
.gtr-container-x7y8z9 table {
min-width: auto;
}
}
What Are Welding Cobots?
In today's fast-evolving manufacturing landscape, welding cobots are transforming how we approach metal joining tasks. These collaborative welding robots, often simply called welding cobots, are designed to work alongside human operators without the need for strict separation. Unlike traditional welding robots that operate in isolated cells, cobots emphasize partnership, making them ideal for dynamic environments. This shift reflects broader market trends where welding robot automation is gaining traction, driven by demands for efficiency and safety in industries like automotive and fabrication. As collaborative welding robot systems become more accessible, they're helping businesses of all sizes streamline operations and boost productivity.
How Welding Cobots Work: Core Technologies
At the heart of a welding cobot's functionality lies a suite of advanced technologies that enable seamless human-robot interaction. These systems rely on sophisticated perception tools, such as force sensors that detect contact pressure, vision systems for precise positioning, and collision detection mechanisms to prevent accidents. This setup allows the cobot to "feel" its surroundings and adjust accordingly.
Teaching a cobot to perform welding tasks is remarkably user-friendly. Operators can use hand-guided teaching, where they physically move the robot arm through the desired path, or opt for more traditional programming methods via intuitive software interfaces. This flexibility extends to various welding processes, including MIG, TIG, and spot welding, ensuring compatibility with diverse project needs.
Integration is another key aspect: welding cobots connect smoothly with power sources and control systems from leading brands. What truly sets them apart, though, are their built-in safety features. Without requiring bulky safety fences, these robots operate at reduced speeds and with force limits, enabling safe collaboration in shared workspaces.
Key Advantages of Welding Cobots
Welding cobots offer a compelling array of benefits that address common pain points in welding operations. Here's a closer look at why they're becoming indispensable in automation welding scenarios.
Easy to Program: Even welders without extensive robotics experience can get up to speed quickly. The intuitive interfaces mean less time on training and more on production, making cobot welding solutions perfect for teams transitioning to automation.
Flexible Deployment: In environments with small-batch or custom welding jobs, these robots shine. Their mobility allows easy repositioning, adapting to changing workflows without major overhauls.
Lower Cost Compared to Traditional Options: From initial investment to installation and ongoing training, welding cobots keep expenses down. This affordability opens doors for smaller shops to embrace robotic welding efficiency.
Improved Welding Quality and Consistency: By minimizing human errors like fatigue or inconsistency, cobots deliver precise, repeatable welds every time, enhancing overall product quality.
Enhanced Worker Safety: Taking over hazardous tasks reduces exposure to fumes, heat, and sparks, allowing humans to focus on oversight and creative problem-solving.
These advantages make welding cobots a smart choice for businesses seeking reliable, efficient automation.
Welding Cobots vs. Traditional Welding Robots
When deciding between a welding cobot and a traditional welding robot, understanding the differences is crucial. Here's a side-by-side comparison to highlight why many are opting for cobots in today's market.
Comparison Point
Welding Cobot
Traditional Welding Robot
Programming
Simple and intuitive, often hand-guided
Requires professional engineers and complex coding
Safety
Human-robot collaboration without fences
Needs large safety enclosures to isolate the robot
Cost
Generally lower upfront and operational expenses
Higher due to equipment, setup, and maintenance
Application
Ideal for small batches and varied tasks
Best for high-volume, repetitive production
Flexibility
High; easy to move and reconfigure
Suited for fixed, dedicated setups
This contrast underscores a key question: Why choose welding cobots? For operations valuing adaptability and cost-effectiveness over sheer volume, they're often the superior option in welding robot automation.
Typical Applications of Welding Cobots
Welding cobots are finding their place across a variety of settings, proving their versatility in industrial welding robot scenarios. In small metal fabrication shops, they handle intricate jobs that require precision without overwhelming the workspace. Automotive parts manufacturing benefits from their ability to weld components efficiently, supporting just-in-time production.
For sheet metal and lightweight structural pieces, cobots excel in delivering clean, consistent results. Custom part processing is another sweet spot, where their flexibility accommodates unique designs. Even in educational and training centers, these automated welding systems serve as hands-on tools for teaching future welders.
Perhaps most notably, they're aiding small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in their shift toward smart manufacturing, making cobot welding applications a gateway to broader automation.
How to Choose the Right Welding Cobot
Selecting the best welding cobot involves matching it to your specific needs. Start by considering the welding type—MIG for heavy-duty joins, TIG for finer work, or spot welding for quick assembly. Payload capacity and reach radius are critical; ensure the cobot can handle your materials and workspace layout.
Compatibility with welding power sources from brands like Fronius, Lincoln, OTC, or Miller is essential for smooth integration. Prioritize user-friendly teaching methods, especially if your team lacks robotics expertise. Don't overlook post-purchase support: reliable maintenance, service, and spare parts availability can make or break long-term success.
Finally, assess how well the cobot fits your production scale and tasks—whether it's high-mix low-volume or something more specialized—to maximize ROI in collaborative welding robot systems
Future Trends of Welding Cobots
Looking ahead, welding cobots are poised for exciting advancements that blend intelligence with practicality. AI-driven path optimization will refine welding routes in real-time, reducing material waste and time. Adaptive welding techniques, where the robot adjusts parameters on the fly based on material variations, promise even greater precision.
Visual recognition and seam tracking will become standard, allowing cobots to follow welds autonomously with minimal setup. Integration with mobile platforms like AGVs or AMRs could create flexible welding cells that move around factories as needed.
As these innovations unfold, expect wider adoption among SMEs, democratizing AI welding cobot technology and pushing smart welding robot solutions into mainstream use for intelligent robotic welding.
Conclusion
In summary, welding cobots represent a powerful fusion of technology and human ingenuity, delivering efficiency, safety, and quality in ways traditional systems can't match. Their rise as a mainstream choice in the metal processing industry stems from addressing real-world challenges like cost barriers and skill shortages. If you're exploring ways to elevate your operations, diving deeper into welding robot automation and collaborative welding robot systems could be the next step. Consider how these tools might fit your setup— the future of welding is collaborative, and it's here now.
View More
The Collaborative Robot Revolution: Flexible Manufacturing Solutions for the Era of Human-Machine Integration
2025-06-10
Driven by the dual forces of the restructuring of global value chains and the advancement of the “Made in China 2025” strategy, the manufacturing sector is undergoing a profound transformation from rigid production to flexible manufacturing. According to McKinsey's 2024 Global Manufacturing Report, 83% of industrial companies have identified “flexible production capabilities” as a core KPI for digital transformation. In this context, collaborative robots (Collaborative Robot, Cobot) are emerging as a key solution to the challenges of “high-mix, low-volume” production, thanks to their unique interactive safety, deployment flexibility, and intelligent collaborative capabilities. This article will analyze how collaborative robots are reshaping modern production systems from three perspectives: technical architecture, system integration, and human-machine collaboration.
I. Technical Evolution and System Positioning of Collaborative Robots
1.1 The Technical Essence of Safe Collaboration
The safety of collaborative robots is based on four technical pillars:
Dynamic Force Control System: Real-time monitoring of contact force via six-axis torque sensors. When abnormal contact exceeding 150N is detected, the system can trigger a safety shutdown within 8ms (compliant with ISO 13849 PLd standards)
3D Intelligent Perception: For example, Omron's FH series vision system combined with a ToF depth camera achieves obstacle detection accuracy of ±2mm within a 3m radius
Bionic Mechanical Design: Utilizes lightweight carbon fiber frames (e.g., Universal Robots' UR20 weighs only 64 kg) and joint elastic drive technology
Digital Safety Twin: Simulates human-machine interaction scenarios in a virtual environment; for example, Yaskawa Electric's MotoSim software can simulate 98% of physical collision risks 1.2 The Neural Endpoints of Manufacturing Systems
In the Industry 4.0 architecture, collaborative robots play the terminal role in the “perception-decision-execution” closed-loop system:
Data collection layer: Uploads over 200 dimensions of device status data, such as joint torque and motor current, via the EtherCAT bus at a frequency of 1 kHz
Edge computing layer: Equipped with edge AI chips such as NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin, enabling local visual recognition (e.g., part defect detection with latency
View More
The Truth About Welding Robot Selection: Does Your Scenario Really Require Teach-Free?
2025-05-28
“On the robot must be selected without teaching” ‘fully automated welding = the future of competitiveness’ - the anxiety of the manufacturing industry is being infinitely amplified by the marketing rhetoric. As a deep-rooted welding field for more than 20 years practitioners, I was saddened to see: 60% of the customers in the selection of the early stage of the “technology path dependence”, while ignoring the depth of their own process analysis. This article from the essence of the process, three steps to end the “pseudo-needs”, to find the optimal solution.
Welding scene “three-dimensional positioning method”: first know yourself, and then choose the technology
Dimension 1: process complexity - the starting point for determining “intelligence”.
Simple scene (suitable for traditional teaching robots):
✅ Single type of weld (straight line/ring)
✅ Consistency > 95% (e.g. mass production of automotive exhaust pipes)
✅ ≤ 3 material types (carbon steel/stainless steel/aluminum alloy)
✅ Cost Warning: The payback period for such scenarios can be extended by 2-3 times with strong no-tutorials.
Complex scenarios (no teaching value highlights):
✅ Multi-species and small batch (e.g. customized parts for construction machinery)
✅ Workpiece tolerance > ± 1.5mm (real-time correction)
✅ Dissimilar material welding (steel + copper, aluminum + titanium, etc.)
✅ Typical case: after the introduction of a no-demonstration program in an agricultural machinery enterprise, the commissioning time for production changeover was shortened from 8 hours to 15 minutes
Dimension 2: production volume - to calculate the “automation” of the economic accounts
Formula: Break-even point = equipment cost / (single piece of labor savings × annual output)
When the production volume 20,000 pieces/year and the product life cycle is >3 years, the teaching-free solution is more cost-effective.
Dimension 3: Environmental constraints - the “invisible threshold” of technology implementation
Four major constraints that must be evaluated:
① Workshop dust/oil level (affecting vision system accuracy)
① Workshop dust/oil level (affects vision system accuracy)
② Grid fluctuation range (whether the equipment can work stably under ±15% voltage variation)
③ Spatial accessibility (pipelines/tight spaces require customized robotic arms)
③ Space accessibility (customized robotic arms for pipelines/narrow spaces)
④ Process certification requirements (automotive industry needs to comply with IATF 16949 process specifications)
Process selection of the five “fatal misunderstanding”: to avoid 90% of the customer procurement pit
Myth 1: “Fully automated = completely unmanned”.
Reality: no teaching still need process experts to set quality rules, the blind pursuit of unmanned may lead to a spike in scrap rate
Avoid the pit strategy: require suppliers to provide process parameters debugging interface, retain the key nodes of manual review rights
Myth 2: “The more functions the software has, the smarter it is.”
Truth: Functional redundancy will increase the complexity of operation, a customer purchased “all-in-one” equipment because the operator mistakenly touched the AI button, resulting in batch rework.
Core principle: choose a system that supports modular subscription (e.g., purchase basic positioning functions first, then upgrade as needed).
Myth 3: “Hardware parameters equal actual performance”.
Key indicators disassembled:
Repeat positioning accuracy ± 0.05mm ≠ welding trajectory accuracy (affected by torch deformation, heat input deformation)
Maximum speed 2m/s ≠ effective welding speed (need to consider the acceleration and deceleration process energy stability)
Suggestion: Use the actual workpiece to carry out zigzag trajectory welding, and test the consistency of the depth of fusion at the inflection point.
Myth 4: “One-time investment to end the battle”
Long-term cost list:
Annual fee for software licenses (some vendors charge by number of robots)
Process database update fee (new material adaptation requires the purchase of data packages)
Four Steps to Scientific Decision Making: A Complete Map from Requirements to Landing
Step 1: Digital modeling of the process
Toolkit:
✅ 3D scans of welded seams (to assess trajectory complexity)
✅ Material heat input sensitivity analysis (to determine control accuracy requirements)
✅ Welding process evaluation report (to define certification criteria)
Output: “Digital Portrait of Welding Process” (with 9 dimensions of scoring)
Step 2: Technology Path AB Test
Comparison of program design:
Program A: high-precision demonstration teaching robot + expert process package
Scheme B: Teach-free robot + adaptive algorithm
Test metrics:
✅ First-piece pass rate ✅ Changeover time ✅ Consumables cost/meter welded seam
Step 3: Supplier Capability Penetration Assessment
Soul six-question checklist:
① Can you provide test weldments of the same material? (Rejected generic demo parts)
② Is the algorithm open to process weight adjustment? (Prevent “black box” decision-making)
① Can you provide test weldments of the same material (reject generic demo parts)?
④ Is the after-sales service response time less than 4 hours?
⑤ Does it support acceptance by third-party testing organizations?
⑤ Does it support acceptance by third-party testing organizations?
⑥ Is the sovereignty of data clearly attributed? (Prevent process data from being locked)
Step 4: Small Scale Validation → Rapid Iteration
30-day validation plan template:
Week 1: Basic function acceptance (positioning accuracy, arc stability)
Week 2: Extreme working condition test (large angle climbing welding, strong electromagnetic interference)
Week 3: Production beat challenge (continuous 8-hour full load operation)
Week 4: Cost audit (consumable loss rate, gas consumption comparison)
Conclusion
The end point of welding intelligence is to bring technology back to the essence of the process! When serving a new energy vehicle supplier, we decisively recommended that the robot be retained for the box weld (due to the high consistency of the workpieces), while the non-teaching program was adopted for the shaped joints of the impact beam. This “hybrid intelligence” strategy helped the customer save 41% of the initial investment.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
View More